Different types of solar system kits



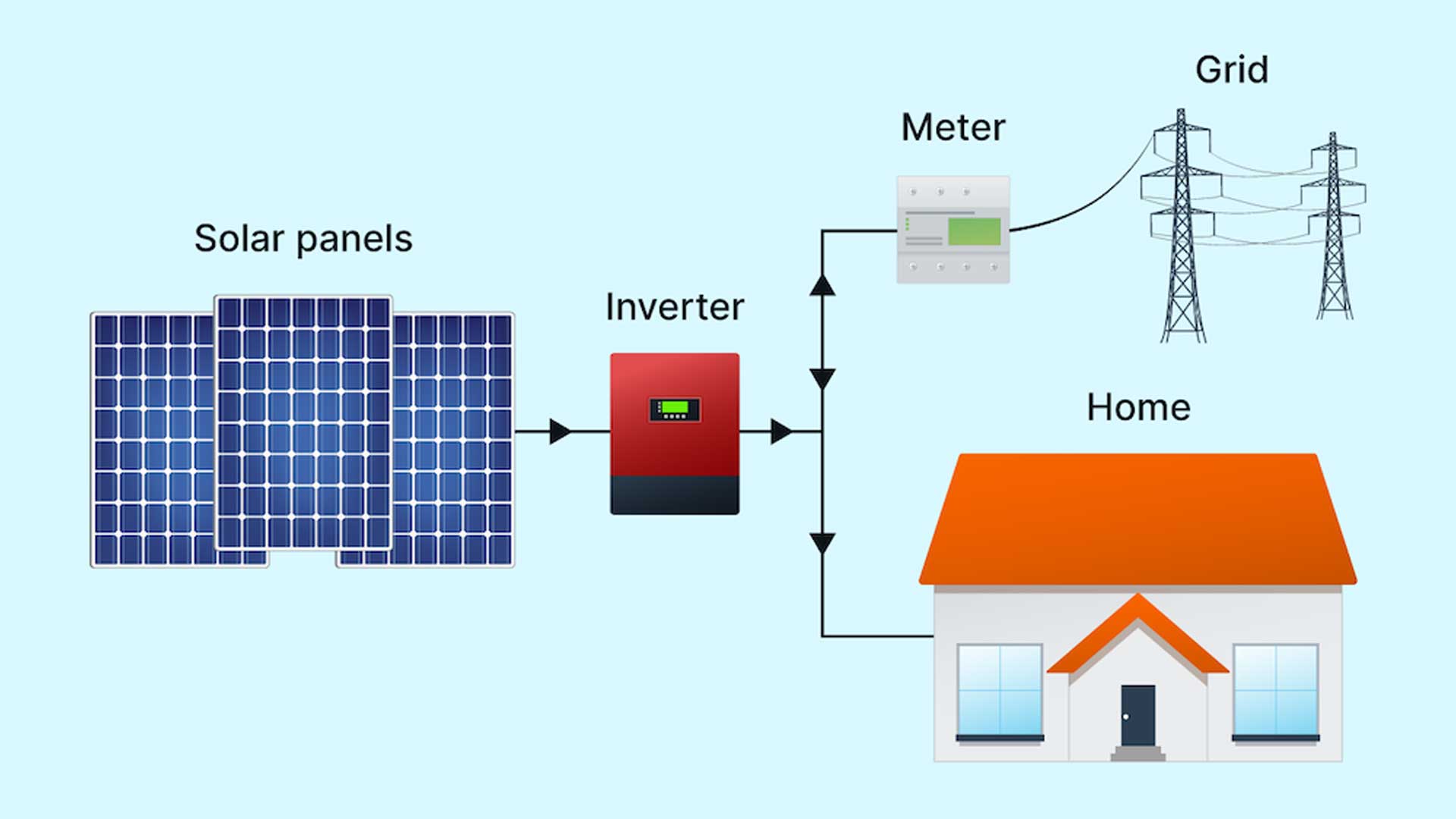
Grid-tied solar system
The Grid-tied solar system is for anyone who is connected to the Eskom power grid. The Grid-tied solar system makes use of Solar PV panels directly connected to the power grid Eskom provides. It allows you to sell the power your system generates and reduces your total energy costs. Grid-tied solar systems are the most affordable solar system option and offers you the quickest payback and return on investment.
Grid-Tie inverter Solar Systems
A grid-tied solar system, also known as an on-grid solar system or grid-connected solar system, is a type of solar energy installation that is connected to the electric grid. In this setup, solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, and any excess energy produced is sent back to the grid. Here’s how a grid-tied solar system works:
- Solar Panels: Solar panels installed on your property capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
- Inverter: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is sent to an inverter. The inverter’s primary function is to convert the DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used by most household appliances and the electric grid.
- Electricity Usage: The AC electricity produced by the inverter is used to power your home’s electrical needs. Any excess electricity that is not immediately consumed by your home is then sent to the grid.
- Metering: Your utility provider installs a special meter called a bidirectional or net meter. This meter measures both the electricity you draw from the grid and the excess electricity you feed back into the grid. This is known as net metering.
- Net Metering: During times when your solar panels generate more electricity than your home uses, the excess energy is fed back into the grid. This causes your net meter to spin backward, effectively providing you with credits for the excess energy you contribute. These credits can be used to offset the cost of electricity you consume from the grid during times when your solar panels aren’t producing enough energy (such as at night or on cloudy days).
- Billing and Cost Savings: At the end of each billing cycle (typically monthly), your utility company calculates the net difference between the electricity you’ve consumed from the grid and the electricity you’ve supplied to the grid. Depending on your local regulations and policies, you might receive a bill for the net amount (if you’ve used more energy than you’ve generated) or a credit for the excess energy (if you’ve generated more energy than you’ve used).
Benefits of a grid-tied solar system include:
- Lower Energy Bills: By generating your own solar energy, you can reduce your reliance on electricity from the grid, leading to lower energy bills.
- Environmental Impact: Grid-tied systems reduce your carbon footprint by using clean and renewable energy sources.
- Net Metering: The ability to feed excess energy into the grid and receive credits can lead to cost savings over time.
- Simplicity: Grid-tied systems are typically simpler to install and maintain compared to off-grid systems.
It’s important to note that grid-tied solar systems rely on the presence of the electric grid. In case of grid outages, most grid-tied systems do not provide power to your home unless you also have battery storage or a backup generator. If you’re interested in energy independence or having power during outages, you might consider a hybrid or off-grid system.

Off-grid solar system
These systems are a great solution for anyone who wants to save money on their electricity costs. In an Off-grid solar system, solar panels are used to charge a bank of batteries. The batteries then provide electricity to your home. Off-grid solar systems are an excellent solution for farmers, people in remote or rural areas, undeveloped land or anyone with no access to Eskom power. This is also a suitable system to be independent of Eskom and providing your own electricity for your home or business. Off-grid solar systems do cost more than other systems due to the battery storage needed to power your home. By using an Off-grid solar system, it is advisable to make some lifestyle changes and use energy-efficient electrical appliances, and also a backup generator could be essential. An off-grid solar system is a standalone solar energy installation that operates independently from the electric grid. It is designed to generate and store its own electricity, allowing you to power your home or other structures without relying on utility-provided electricity. Off-grid systems are commonly used in remote areas where grid access is not available or practical.
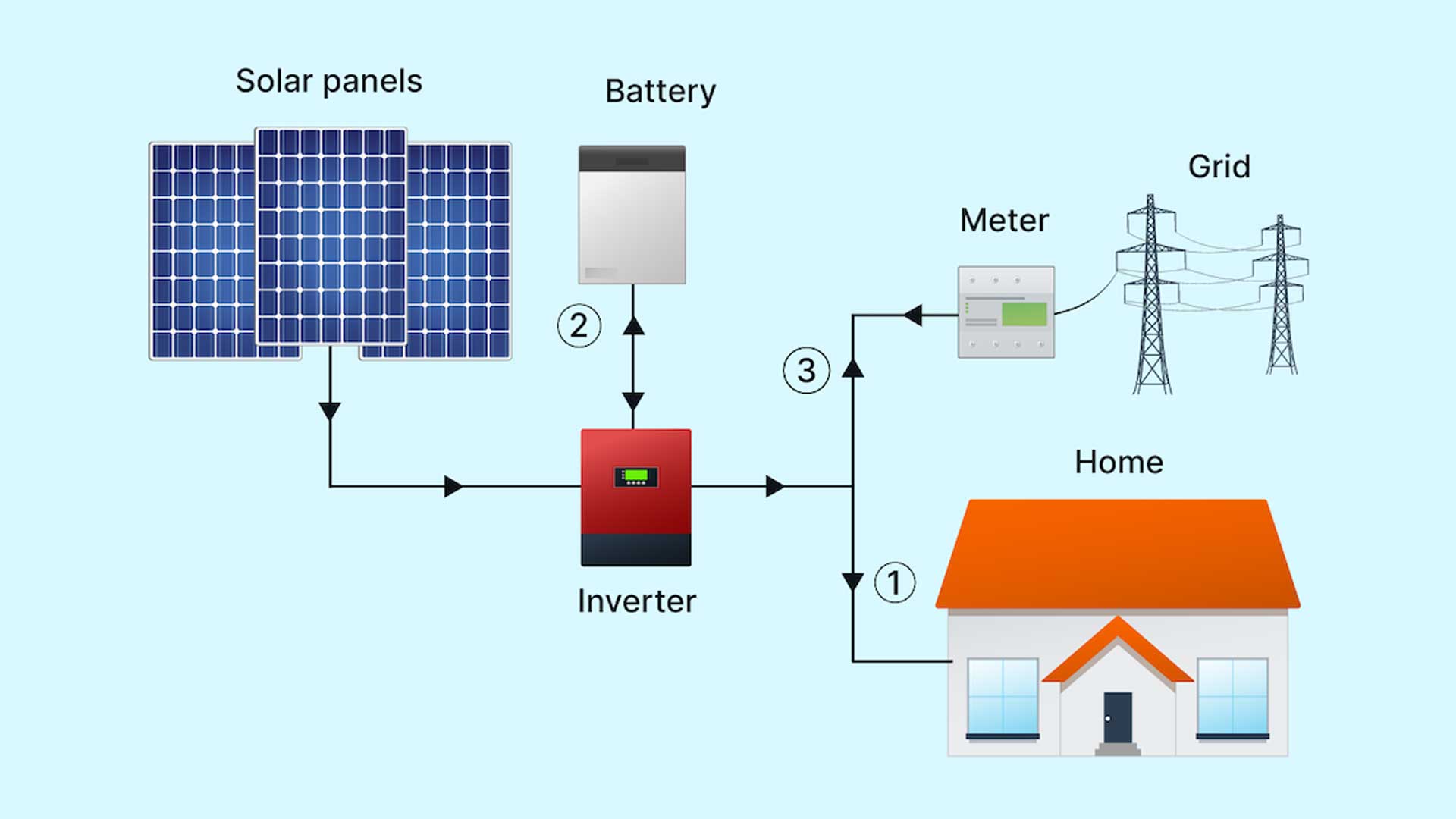
Off-grid inverter solar systems
- Solar Panels: Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity using the photovoltaic effect.
- Charge Controller: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is sent to a charge controller. The charge controller regulates the flow of electricity to the batteries to prevent overcharging and over-discharging, which can damage the batteries.
- Batteries: The energy generated by the solar panels is stored in batteries. These batteries store the excess energy generated during sunny periods so that it can be used during times when the sun isn’t shining (e.g., at night or on cloudy days).
- Inverter: The stored DC electricity in the batteries is sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity for use by household appliances. Some off-grid systems also have inverters with built-in charging capabilities to recharge the batteries from a backup generator when solar energy is insufficient.
- Electricity Usage: The AC electricity produced by the inverter powers your home’s electrical needs, similar to how electricity from the grid would.
- Backup Generator (Optional): In areas with limited sunlight or high energy demands, an optional backup generator can be used to recharge the batteries when solar energy is insufficient. This provides extra power and ensures uninterrupted electricity supply.
Benefits of an off-grid solar system include:
- Energy Independence: Off-grid systems provide complete energy independence, allowing you to generate and store your own electricity without relying on the grid.
- Remote Locations: Off-grid systems are ideal for remote or rural areas where grid access is unavailable or expensive to install.
- Environmental Impact: Off-grid systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels and provide clean and renewable energy, helping to reduce carbon emissions.
However, there are also considerations and challenges with off-grid systems:
- Higher Initial Costs: Off-grid systems typically require more equipment, including batteries and backup generators, which can increase the initial investment.
- Battery Maintenance: Batteries have a limited lifespan and require maintenance, including regular checks and potential replacements.
- Energy Management: Proper energy management is crucial to ensure that energy usage matches generation, especially during periods of low sunlight.
- Sizing and Design: Accurate system sizing and design are essential to ensure the system meets your energy needs without underestimating or oversizing components.
When considering an off-grid solar system, it’s recommended to work with experienced professionals who can design and install a system that suits your energy requirements and location.


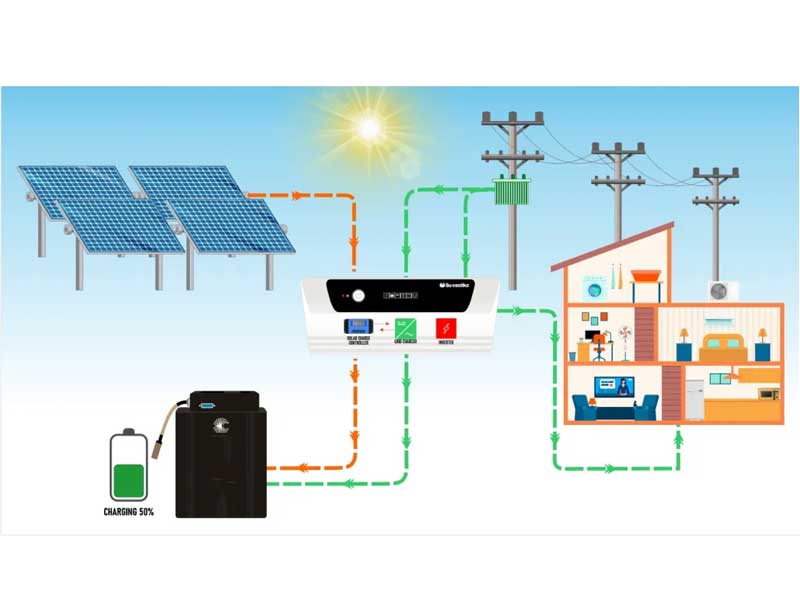
Hybrid solar system
The Hybrid solar system configuration offers you the best of both worlds. It is an ideal system for anyone who has unreliable power, such as load-shedding scenarios. It works best provide power for people who needs a water pump, lights, security systems and office equipment to function. The Grid-tied system with battery backup or hybrid solar kit, is more expensive compared to Grid-tied systems and offers a lower return on investment. However, the Hybrid solar system, is the most reliable solar system kit. The hybrid grid-tied system with battery backup, can act as a grid-tie system by sending electricity back to the grid. It can also charge batteries for powering electrical appliances in your home. A hybrid solar system, also known as a hybrid solar power system or grid-tied hybrid system, combines elements of both grid-tied and off-grid solar systems. It offers the benefits of grid-tied systems while also incorporating energy storage capabilities to provide power during grid outages or when solar energy production is low.
Hybrid inverter solar systems
Here’s how a hybrid solar system works:
- Solar Panels: Like in a standard grid-tied system, solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity using the photovoltaic effect.
- Inverter: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is sent to an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used to power your home’s electrical needs.
- Grid Connection: A hybrid system is connected to the electric grid, allowing you to draw electricity from the grid when your energy demand exceeds the solar energy production or when the battery capacity is low.
- Batteries: One of the key features of a hybrid system is the inclusion of energy storage batteries. These batteries store excess energy generated by the solar panels during sunny periods. The stored energy can then be used during times of high demand, grid outages, or when solar energy production is insufficient.
- Battery Management: A hybrid system’s controller manages the charging and discharging of the batteries. It ensures that the batteries are charged when excess solar energy is available and discharges them when needed, such as during peak energy demand or grid outages.
- Backup Generator (Optional): Some hybrid systems also allow for the integration of a backup generator. This generator can be used to recharge the batteries during extended periods of low sunlight or high energy demand, providing an additional source of power.
Benefits of a hybrid solar system include:
- Energy Independence: Hybrid systems provide a level of energy independence by incorporating energy storage to use during grid outages or when solar energy is low.
- Increased Self-Consumption: The energy storage component allows you to increase your self-consumption of solar energy, reducing reliance on electricity from the grid.
- Backup Power: The battery storage provides backup power during grid outages, ensuring that essential appliances continue to function.
However, hybrid systems also have considerations and challenges:
- Initial Investment: Hybrid systems typically have higher upfront costs due to the inclusion of batteries and energy storage equipment.
- Battery Maintenance: Batteries have a limited lifespan and require maintenance, including monitoring and potential replacements.
- Sizing and Design: Proper system sizing and design are essential to ensure that the battery capacity matches your energy needs.
Hybrid solar systems are a suitable choice for homeowners who want to maximize their use of solar energy, increase their energy self-sufficiency, and have the option for backup power. When considering a hybrid system, it’s recommended to consult with solar professionals who can design a system that meets your energy requirements and provides the desired level of energy independence.



Battery backup systems
Battery backup systems usually receives their power from the grid and is usually installed without solar panels. When there is power from the grid, the batteries are charged. The Battery backup systems are ideal for businesses and households that require emergency backup power in case of power outages. Most customers start off with battery backup systems and later add solar panels to complete their conversion to solar energy. Battery backup systems, also known as energy storage systems, are components that store excess electricity generated by solar panels or other energy sources for later use. These systems provide a reliable source of backup power during grid outages or when energy production is low. Battery backup systems can be integrated into grid-tied, off-grid, or hybrid solar installations.
How Battery Backup Systems Work:
- Charging: When your solar panels or other energy sources generate more electricity than your immediate consumption, the excess energy is directed to charge the batteries.
- Energy Storage: The charged batteries store the excess energy in the form of direct current (DC) electricity. This stored energy can be used later when needed.
- Inverter: When you need to use the stored energy, an inverter converts the DC electricity from the batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity, which can power your home’s electrical loads.
- Backup Power: In the event of a grid outage or when solar energy production is insufficient, the battery backup system automatically switches to using the stored energy to power your essential appliances or entire home, depending on the system’s capacity.
Benefits of Battery Backup Systems:
- Grid Outage Protection: Battery backup systems provide a reliable source of power during grid outages, ensuring that you have electricity for critical appliances and systems.
- Energy Self-Sufficiency: Battery systems increase your self-consumption of solar energy by allowing you to use the excess energy produced during the day at night or during cloudy periods.
- Time-of-Use Optimization: In regions with time-of-use electricity pricing, you can use stored energy during peak hours when electricity costs are higher, saving you money on your utility bills.
- Peak Demand Reduction: Battery systems can help reduce peak demand on the grid during times when electricity demand is highest, contributing to grid stability.
- Environmental Impact: Using stored solar energy during peak demand or grid outages reduces the need for fossil fuel-based backup generators, contributing to a cleaner energy mix.
- Increased System Flexibility: Battery backup systems can be integrated into grid-tied and hybrid solar installations, offering increased energy management options.
Considerations and Challenges:
- Initial Investment: Battery backup systems add to the initial cost of a solar installation, including the batteries, inverter, and associated equipment.
- Battery Maintenance: Batteries have a limited lifespan and require maintenance, monitoring, and potential replacements.
- Sizing and Capacity: Properly sizing the battery system to match your energy needs is crucial for effective backup power.
- System Integration: Compatibility between your solar panels, inverters, and battery system is essential for efficient energy storage and usage.
- Local Regulations and Incentives: Battery backup systems might be subject to local regulations and incentives that vary by region.
When considering a battery backup system, it’s advisable to work with experienced solar professionals who can assess your energy needs, recommend appropriate system sizing, and install a system that aligns with your goals and requirements.

