Battery charging methods
There are a few common methods for charging batteries, each with its own advantages and considerations. The choice of method depends on the type of battery, its chemistry, and the application.

Constant Voltage Charging (CV)
This is a simple method where a constant voltage is applied to the battery terminals. As the battery charges, the current gradually decreases. Once the battery reaches its full capacity, the charging process stops or enters a trickle charge mode. This method is commonly used for lead-acid batteries and some types of lithium-ion batteries. A constant voltage battery charger is a DC power supply which basically made up from a step-down transformer from the mains with a rectifier that provides the DC voltage which ultimately charges the battery. These forms of charging can be commonly found in inexpensive vehicle battery chargers. Backup batteries and car batteries, usually use lead-acid cells which requires constant voltage chargers. On the other hand, a constant voltage system is used with lithium-ion batteries. However, lithium-ion constant voltage systems usually consist of added circuitry which acts as a protection layer for the battery and the operator.
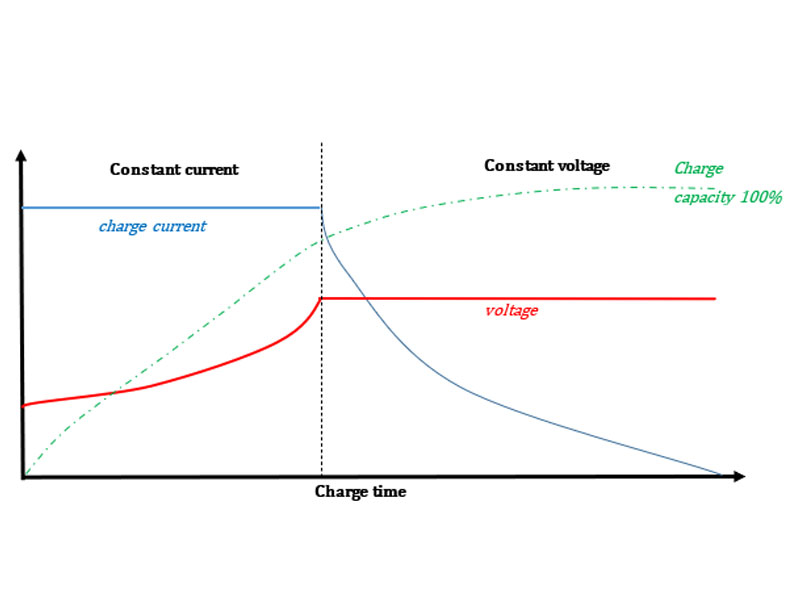


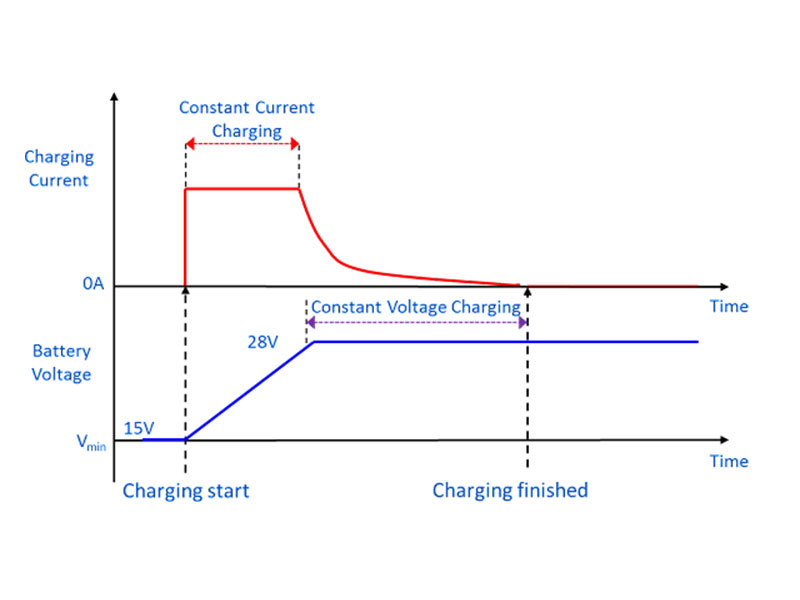
Constant Current Charging (CC)
In this method, a constant current is applied to the battery until it reaches a predefined voltage level. This is often used for lithium-ion batteries and is particularly useful in the initial stages of charging when the battery voltage is low.


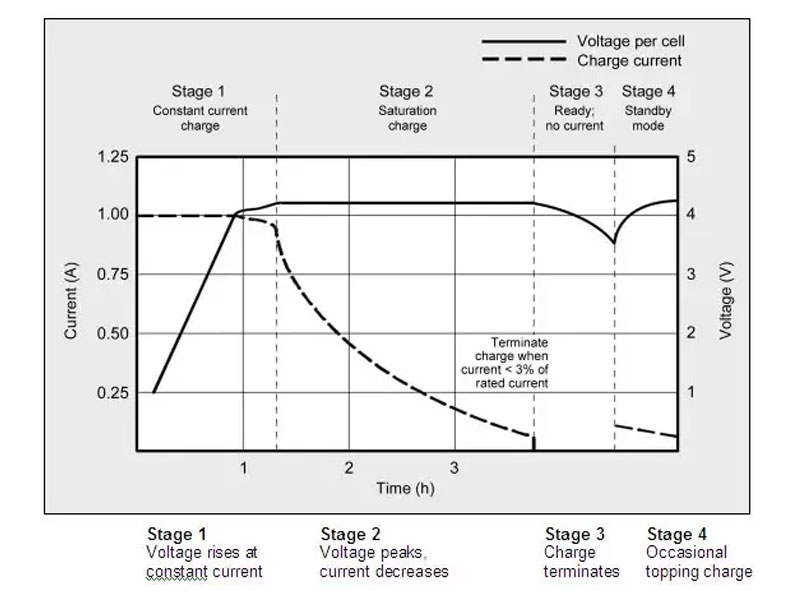
Trickle Charging
After a battery is fully charged using CV or CC methods, a trickle charge may be applied to maintain the battery’s charge at a certain level. This prevents self-discharge and keeps the battery ready for use. Trickle charging is often used for applications where the battery remains connected to a charger for extended periods, such as in backup power systems.


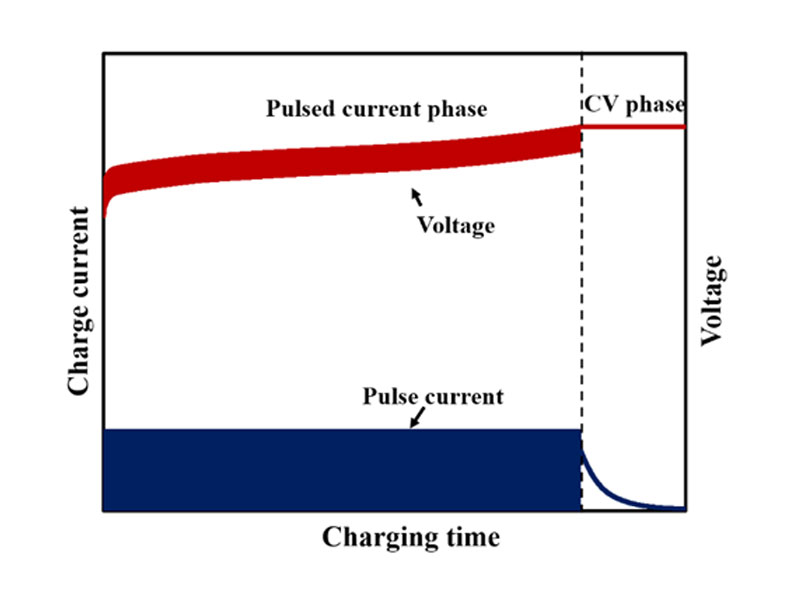
Pulse Charging
This method involves sending short pulses of current to the battery. It’s used to reduce battery sulfation (the build-up of lead sulphate crystals on lead-acid batteries’ plates) and extend battery life. Pulse battery chargers uses pulses of current to charge a battery. Based on the average current of pulses, the charging rate can be accurately controlled by varying the width of the pulses which is commonly about a second. When the charging process is initiated, there are short rest periods of a few milliseconds between charging pulses, which allow chemical actions in the battery to stabilize. Therefore, allowing chemical reactions inside the battery to keep the correct pace with the charging rate of electrical energy.



Fast Charging
Fast charging methods aim to charge a battery quickly, often by increasing the charging current or voltage. This can be useful for applications where rapid charging is required, such as in electric vehicles and smartphones. However, fast charging can generate more heat and might require additional battery management systems to ensure safety.


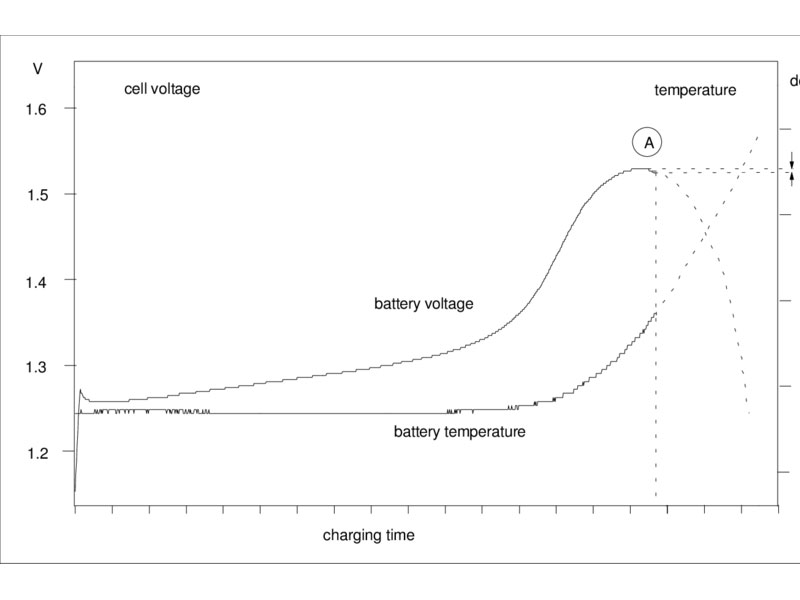
Delta-V Charging
This method is often used for NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) and NiCd (Nickel-Cadmium) batteries. It involves monitoring the change in voltage during charging. When the voltage reaches a specific point, the charger reduces the charging current or switches to trickle charge mode.


Smart Charging
Advanced battery management systems (BMS) can implement algorithms that adapt the charging process based on various factors, such as battery temperature, state of charge, and age. This helps optimize charging for safety and longevity.



Solar Charging
Solar panels can be used to charge batteries, typically by employing charge controllers that regulate the charging process to prevent overcharging and damage.
Battery charging information
Using a battery charger is a great solution to ensure that the batteries have sufficient energy when they are required. However, there are some important things to remember when using battery chargers.
- If a battery is discharged, it is a best practice to recharge the battery as soon as you could. If a discharged battery is left without recharging for a long period of time, the battery can be damaged and would most likely need to be replaced.
- Always ensure that the battery being charged is correctly connected. A reverse connection may cause serious damages to the battery.
- Inspect all the discharged batteries before you initiate the charging process. In many cases, batteries might be damaged which can result in a release of battery acid escaping the battery or gasses being discharged. This can be hazardous to the operator.
- Ensure to always use the correct battery charger for the specific battery which it should be associated with. Not all battery chargers work with the same type of batteries.
Charging method conclusion
When selecting a charging method, it’s crucial to consider the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific type of battery you’re using. Different chemistries (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion, NiMH) have distinct charging requirements to ensure safety, performance, and longevity.

